| Center for Energy, Environmental, and Economic Systems Analysis (CEEESA) |  |
Research Areas:
Energy, Environment, and
Economics
National and Homeland
Security
Infrastructure Assurance
Emergency Preparedness
Social Dynamics
Policy Analysis
Core Capabilities:
Systems Analysis
Modeling, Simulation, and
Visualization
Complex Adaptive Systems
Decision Support and Risk
Management
Information Sciences
Assisting Mexico in Developing Energy Supply and Demand Projections
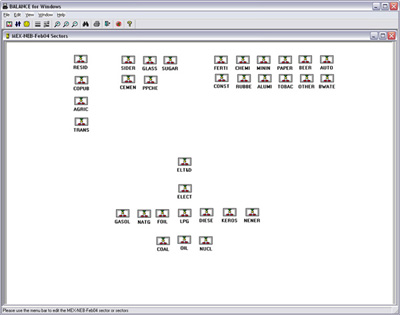
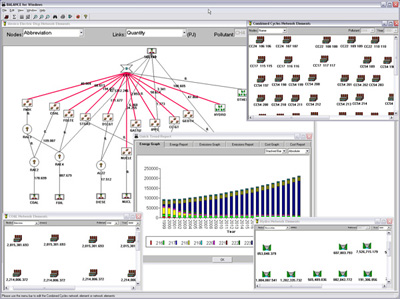
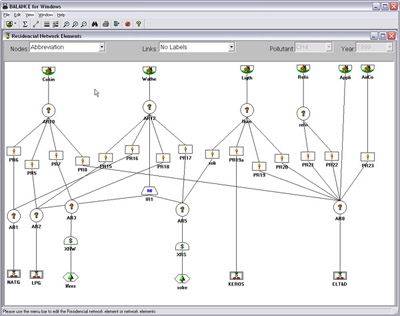
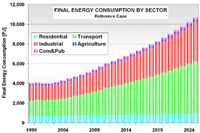
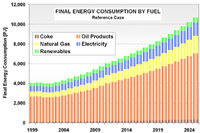
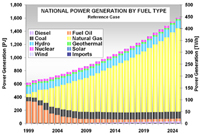
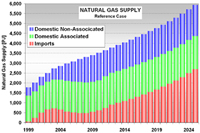
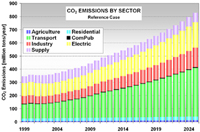
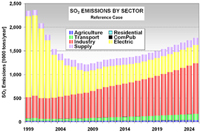
Methodology: CEEESA and the team of experts from Mexico analyzed the country's entire energy supply and demand system using CEEESA's latest version of the popular ENPEP-BALANCE software. The team developed a system representation, a so-called energy network, using ENPEP's powerful graphical user interface. The screen captures below show examples of the Mexican ENPEP-BALANCE network. The first screen shows the general energy network representation with all the economic sectors included in the analysis. In addition to 3 resource supply sectors, the network includes 9 conversion and distribution sectors as well as 21 demand sectors. Industry is divided into 17 individual industrial branches. Each of the sectors is developed at different levels of detail depending on data availability and analytical needs. Click on the picture to see a larger version of the screenshot. The following screen capture shows Mexico's power sector representation. The model allows a unit-by-unit representation of the power generation sector. The user can look at various results at the same time. The screenshot below shows the different fuel groups as well as some of the individual combined cycle units, coal units, and hydro-electric plants. For the coal units, the user is viewing annual CO2 emissions. For the hydro plants, the user is looking at the annual generation. And for the combined cycle units, the user chose to view the unit names. At the same time, using the new Quick report feature, the user can view, for example, the generation by fuel group by highlighting the desired links (selected links turn red) and opening the report graph. Click on the picture to see a larger version of the screenshot. The next screen capture shows the residential sector representation. The team is modeling different end use categories (useful energy demand), such as cooking, water heating, lighting, refrigeration, air conditioning, and appliances. Different technologies compete to provide this service. Click on the picture to see a larger version of the screenshot. The detailed model configuration allows the team to look at a variety of supply and demand issues. In addition, the model is configured to estimate emissions of CO2, SO2, NOX, PM, and other pollutants. The team completed their base case and evaluated several alternative development scenarios. This project is a follow-up to an earlier study that analyzed Mexico's power system in detail. The earlier study investigated the economic and environmental impacts of a total of 14 electric system expansion scenarios, including limitations of gas supply, various fuel price scenarios, different levels of reliability and reserve margins, forced nuclear, etc. The power sector analysis was conducted with the IAEA's DECADES tools. Click here to see more information on Mexico's power sector analysis. Results: The detailed model configuration allows the team to look at a variety of supply and demand issues. In addition, the model is configured to estimate emissions of CO2, SO2, NOX, PM, and other pollutants. The team finalized the analysis in early 2003 and presented the results for a Reference Case and 3 Alternative Scenarios at a seminar at SENER in February 2003. Following are a few graphs that show for the Reference Scenario the projected energy demand by sector and by fuel, the forecast for power generation by fuel type, the future natural gas supply by source, and the projected CO2 and SO2 emissions by sector. In the Additional Resources section below, you will find files with additional results.
Training and Capacity Building: As part of the project, CEEESA has transferred the model to participating institutions. A 2-week training course was held in September 2000 followed by several one-week site visits by CEEESA staff members to Mexico. Also assisting the team are experts from the Colombian Ministry of Energy (UPME) and the Brazilian Electricity Company CEMIG. UPME and CEMIG have used ENPEP-BALANCE for their analysis needs for years and are able to help the team in addressing region-specific issues. CEEESA has extensive expertise and experience in capacity building by assisting our ENPEP-BALANCE users around the world in the form of training and implementation support. Over the last 25+ years, we have conducted training courses in many locations around the world and have successfully trained over 1300 experts from more than 90 countries in the use of our tools. ENPEP-BALANCE is actively in use in many of these countries. ENPEP-BALANCE training courses and workshops can be tailored to your specific needs and can last anywhere between a few days to a couple of weeks. Courses may be held at Argonne's facility in the Chicago area or at your facilities. Click here for information on past and upcoming training courses or click on the pictures below. Additional Resources: For more information on this application and the ENPEP-BALANCE model, download the following brochures, presentations, and papers in pdf format:
For more information, contact contact CEEESA |
| U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science | UChicago Argonne LLC |
| Privacy & Security Notice | Contact Us | Search |
 Background: The Center for Energy, Environmental, and Economic Systems Analysis (CEEESA) collaborated with several institutions in Mexico on implementing ENPEP-BALANCE to analyze that country's future energy needs and to estimate the associated environmental burdens. Participating Mexican institutions include the Ministry of Energy (SENER), the Electricity Company (CFE), the oil company (PEMEX), the National Autonomous University (UNAM), the Mexican Petroleum Institute (IMP), the National Ecology Institute (INE), and the National Commission for Energy Conservation (CONAE). The project is supported by the U.S. Government and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in Vienna and has a strong focus on capacity building in energy and environmental analysis.
Background: The Center for Energy, Environmental, and Economic Systems Analysis (CEEESA) collaborated with several institutions in Mexico on implementing ENPEP-BALANCE to analyze that country's future energy needs and to estimate the associated environmental burdens. Participating Mexican institutions include the Ministry of Energy (SENER), the Electricity Company (CFE), the oil company (PEMEX), the National Autonomous University (UNAM), the Mexican Petroleum Institute (IMP), the National Ecology Institute (INE), and the National Commission for Energy Conservation (CONAE). The project is supported by the U.S. Government and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in Vienna and has a strong focus on capacity building in energy and environmental analysis.