| Center for Energy, Environmental, and Economic Systems Analysis (CEEESA) |  |
Research Areas:
Energy, Environment, and
Economics
National and Homeland
Security
Infrastructure Assurance
Emergency Preparedness
Social Dynamics
Policy Analysis
Core Capabilities:
Systems Analysis
Modeling, Simulation, and
Visualization
Complex Adaptive Systems
Decision Support and Risk
Management
Information Sciences
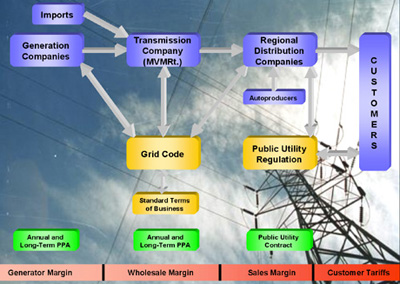
Evaluating Independent Power Producer (IPP) Bids for the Hungarian Power Companies Ltd. (MVMRt.)
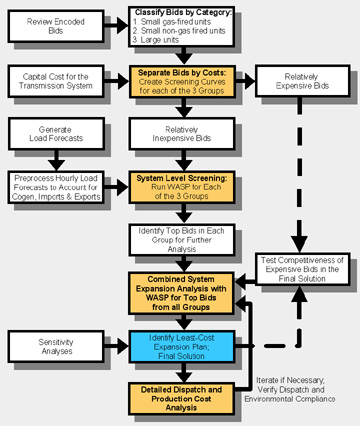
Methodology: Experts from the Center for Energy, Environmental, and Economic Systems Analysis (CEEESA) teamed with a Hungarian consulting company to develop the bid evaluation methodology and act as technical auditor to MVMRt. during the evaluation phase. CEEESA staff members designed the methodology to make full use of MVMRt.'s current electric system analysis tools, which included the WASP-III Plus model within the Argonne-developed Energy and Power Evaluation Program (ENPEP). The CEEESA methodology provided a comprehensive and consistent bid evaluation framework. The use of the well-established WASP-III Plus model ensured the acceptance of the results by all bidders. Scope of Work: The figure below shows the analysis framework. Each bid was encoded with a unique identification number and grouped into three categories according to tender number, fuel type, and size. An initial pass-through identified the relatively expensive proposals in each group. CEEESA used screening curves to rank the proposals in this step. Costs included capacity and energy charges, plus any transmission costs.
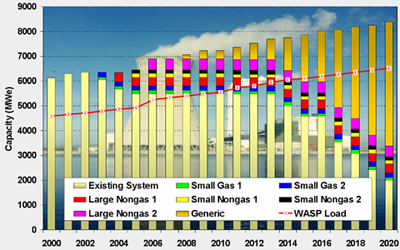
The best proposals advanced to the system-level screening with the WASP-III Plus model to determine the most economical expansion plan for Hungary’s power generating system under two load forecasts. CEEESA staff identified the top bids in each of the three groups under both load forecasts and completed a combined analysis of the top bids from all three groups, taking into account the plant mix and natural gas capacity constraints specified in the tender documents. CEEESA experts transferred the preliminary results to a detailed dispatch and production cost model and identified the winning bidders when results from both models converged. CEEESA staff also performed a sensitivity analysis for such key parameters as discount rate, loss of load probability, and cost of energy-not-served. Finally, CEEESA completed a combined analysis of the proposals that were not selected during the initial screening to test the competitiveness of these bids against those that were selected. Results of Analysis: On the basis of CEEESA’s evaluation, MVMRt. signed two long-term power purchase agreements worth an estimated US$1.3 billion. The candidates include a 191-MWe gas-fired, combined-cycle unit and a 110-MWe cogeneration combined-cycle plant. Based on 7,000 hours of annual operation, the first contract will cost 6.43 Hungarian Forint per kilowatt-hour and the second will cost 6.87 Hungarian Forint per kilowatt-hour.
Training and Capacity Building: In a follow-on project, CEEESA provided training in the WASP-IPP evaluation methodology as well as the GTMax model to several staff members of MVMRt. CEEESA has extensive expertise and experience in capacity building by assisting our model users around the world in the form of training and implementation support. For more than 25 years, we have conducted training courses in many locations around the world and have successfully trained over 1,300 experts from more than 90 countries in the use of our tools. Our models are actively in use in many of these countries.
GTMax training courses and workshops can be tailored to your specific needs and can last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks. Courses may be held at Argonne's facility in the Chicago area or at your facilities. Click here for information on past and upcoming training courses. Additional Resources: For more information on this application and the ENPEP model, download the following brochures, presentations, and papers in pdf format:
For more information, contact contact CEEESA |
| U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science | UChicago Argonne LLC |
| Privacy & Security Notice | Contact Us | Search |
 Background: At the end of 1997, the Hungarian Power Companies Ltd. (MVMRt.) issued two tenders for independent power producer (IPP) bids to increase power generating capacity in Hungary. The first, covering the period from 2001 to 2003, involved
600-1,000 MWe of generating capacity using small- to medium-sized units (20-200 MWe). The second, covering the period from 2004 to 2006, was based on a total capacity of 800-1,400 MWe using greater than 200-MWe units. MVMRt. received 33 technical and financial bids to supply this new power and needed a consistent, efficient method to evaluate the bids.
Background: At the end of 1997, the Hungarian Power Companies Ltd. (MVMRt.) issued two tenders for independent power producer (IPP) bids to increase power generating capacity in Hungary. The first, covering the period from 2001 to 2003, involved
600-1,000 MWe of generating capacity using small- to medium-sized units (20-200 MWe). The second, covering the period from 2004 to 2006, was based on a total capacity of 800-1,400 MWe using greater than 200-MWe units. MVMRt. received 33 technical and financial bids to supply this new power and needed a consistent, efficient method to evaluate the bids.