CEEESA Natural Gas Systems Analysis Tools
The Center for Energy, Environmental, and Economic Systems Analysis (CEEESA) provides natural gas systems analysis tools that cover a wide range of issues. The table below summarizes the available models. Click on each model name to get more information.
Energy and Power Evaluation Program (ENPEP-BALANCE)
 The Windows version of the Energy and Power Evaluation Program (ENPEP-BALANCE) is the premier energy systems analysis software in use in over 80 countries. ENPEP-BALANCE
was developed by CEEESA with support from the U.S. Department of
Energy. ENPEP-BALANCE allows users to evaluate the entire energy system (supply and demand side) and the environmental implications of different energy strategies. The
latest ENPEP-BALANCE version takes full advantage of the Windows operating environment. The Windows version of the Energy and Power Evaluation Program (ENPEP-BALANCE) is the premier energy systems analysis software in use in over 80 countries. ENPEP-BALANCE
was developed by CEEESA with support from the U.S. Department of
Energy. ENPEP-BALANCE allows users to evaluate the entire energy system (supply and demand side) and the environmental implications of different energy strategies. The
latest ENPEP-BALANCE version takes full advantage of the Windows operating environment.
The nonlinear equilibrium ENPEP-BALANCE model matches the demand for energy with available resources and technologies. Its market-based simulation approach allows ENPEP-BALANCE to determine the responses of various segments of the energy system to changes in energy prices and demand levels. The model relies on a decentralized decision-making process in the energy sector, and it can be calibrated to the different preferences of energy users and suppliers. ENPEP-BALANCE uses a network that consists of different nodes and links, which represent various energy systems. Nodes in the network represent depletable and renewable resources, various conversion processes, refineries, thermal and hydro power stations, cogeneration units, boilers and furnaces, marketplace competition, taxes and subsidies, and energy demands. Links connect the nodes and transfer information among nodes.
ENPEP-BALANCE is very versatile in that the analyst starts with an empty workspace and builds an energy system configuration of nodes and links. ENPEP-BALANCE's powerful graphical user interface makes it as easy as “drag and drop” to build networks of regional, national, or multinational scope. Drop-down menus can be used to display model inputs and results directly within the energy network. Double-clicking the nodes allows access to more detailed information. The latest ENPEP-BALANCE version also incorporates calculations of environmental residuals, such as atmospheric pollution, water effluents, and waste generation. ENPEP-BALANCE is used extensively in the global community to conduct greenhouse gas mitigation analyses, energy policy studies, and natural gas market analyses.
Click here for more details on the ENPEP-BALANCE model.
For more information about Energy and Power Evaluation Program (ENPEP-BALANCE), contact CEEESA.
Geographic Analysis System for Market Assessment and Planning (GASMAP)
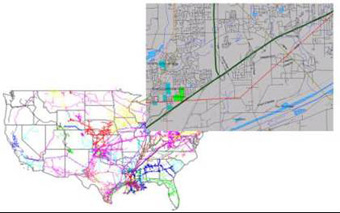 GASMAP combines a geographic information system and a relational database system that provide information on the U.S. natural gas infrastructure. GASMAP can be used to locate the pipelines of any gas transmission company on a map at varying levels of detail. Users can then access Information on capacity (pipe diameter, length, and maximum operating pressure); flows (peak day, average day, receipt and delivery points, storage, and delivery volume); and financial parameters (gas purchases, gas prices, sales volumes, operating and maintenance costs, and balance sheet). Because GASMAP is loaded on a remote server, multiple users can access information from their own locations. GASMAP combines a geographic information system and a relational database system that provide information on the U.S. natural gas infrastructure. GASMAP can be used to locate the pipelines of any gas transmission company on a map at varying levels of detail. Users can then access Information on capacity (pipe diameter, length, and maximum operating pressure); flows (peak day, average day, receipt and delivery points, storage, and delivery volume); and financial parameters (gas purchases, gas prices, sales volumes, operating and maintenance costs, and balance sheet). Because GASMAP is loaded on a remote server, multiple users can access information from their own locations.
For more information about Geographic Analysis System for Market Assessment and Planning (GASMAP), contact CEEESA.
NGview
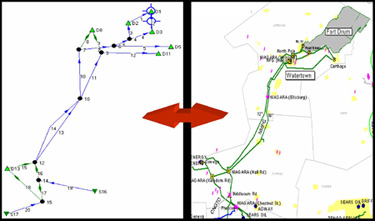 NGview decreases the time required to develop a natural gas network topology, including pipeline links (uni- or bi-directional) and pipeline nodes (e.g., delivery points, supply points, and interconnections). NGview helps link spatial and relational data sets, which could include thousands of pipeline segments and points. Once these links have been established, data can be updated with minimal effort, providing quick turnaround time for studies. The model’s database interface links to simulation tools, such as NGflow and NGcut. NGview greatly improves the viewing and understanding of simulation results because analysts can toggle between schematic and geographical information system views. NGview decreases the time required to develop a natural gas network topology, including pipeline links (uni- or bi-directional) and pipeline nodes (e.g., delivery points, supply points, and interconnections). NGview helps link spatial and relational data sets, which could include thousands of pipeline segments and points. Once these links have been established, data can be updated with minimal effort, providing quick turnaround time for studies. The model’s database interface links to simulation tools, such as NGflow and NGcut. NGview greatly improves the viewing and understanding of simulation results because analysts can toggle between schematic and geographical information system views.
For more information about NGview, contact CEEESA.
NGflow
NGflow identifies critical links and nodes in a network topology. This tool provides an alternative to using very detailed, data-intensive commercial flow simulation models. NGflow simulates steady-state gas network flows and provides gas flow movements under various operating conditions based on gas flow balancing algorithms and available system flow data. The model also gives a unique snapshot of the gas transmission infrastructure that supports a certain location or site. NGflow is used extensively in analyses of U.S. natural gas network issues.
For more information about NGflow, contact CEEESA.
NGdepletion
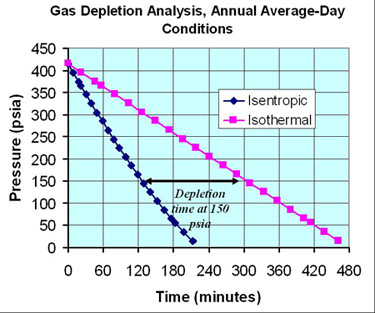 NGdepletion addresses outage duration times and determines whether and when a component outage will affect a specific location or site. The model computes the amount of time that the line pack will be able to continue to supply gas. NGdepletion is used extensively in analyses of U.S. natural gas network issues and in studies of electricity-gas interdependency issues. NGdepletion addresses outage duration times and determines whether and when a component outage will affect a specific location or site. The model computes the amount of time that the line pack will be able to continue to supply gas. NGdepletion is used extensively in analyses of U.S. natural gas network issues and in studies of electricity-gas interdependency issues.
For more information about NGdepletion, contact CEEESA.
NGpressure
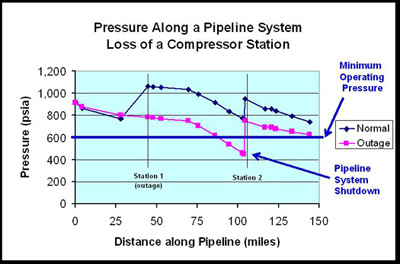 NGpressure determines how the loss of a critical link or node under various operating conditions might affect a natural gas system. The model addresses central issues such as: “Can the system continue to deliver gas to a certain location or site if a key city-gate is disrupted under both average and peak day conditions?” The model is based on the premise that the ability of a pipeline to deliver natural gas depends directly on operating pressure. NGpressure uses standardized industry equations and various data sources, and it is used extensively in analyses of issues associated with the U.S. natural gas network. NGpressure determines how the loss of a critical link or node under various operating conditions might affect a natural gas system. The model addresses central issues such as: “Can the system continue to deliver gas to a certain location or site if a key city-gate is disrupted under both average and peak day conditions?” The model is based on the premise that the ability of a pipeline to deliver natural gas depends directly on operating pressure. NGpressure uses standardized industry equations and various data sources, and it is used extensively in analyses of issues associated with the U.S. natural gas network.
For more information about NGpressure, contact CEEESA.
NGcut
NGcut determines network component failure sets that could isolate a specific location or site from all supply sources. One of the advantages of using this model is that it significantly decreases the time needed to analyze site isolation issues by automating the construction of failure sets. The model also allows analysts to consider a larger number of failures and to broaden an analysis. NGcut is used extensively in analyses of issues associated with the U.S. natural gas network.
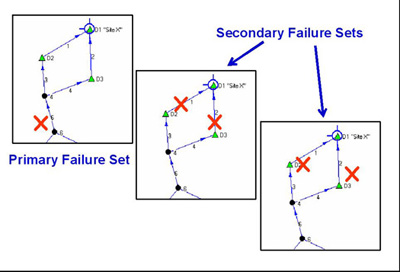
For more information about NGcut, contact CEEESA.
NGlocator
This geographic information system-based tool quickly identifies distribution companies for areas or sites. It improves the efficiency of natural gas analysis by reducing the time needed to identify local distribution companies and to assemble background data for the local infrastructure network. It also provides reports and maps that are helpful in conducting analyses.
For more information about NGlocator, contact CEEESA.
NGanalyzer
NGanalyzer assists users in analyzing identified gas engineering vulnerabilities, such as the number of city-gates, available storage, and pipeline capacity and interconnection. NGanalyzer is used extensively in analyses of issues associated with the U.S. natural gas network.
For more information about NGanalyzer, contact CEEESA.
|

 The Windows version of the Energy and Power Evaluation Program (ENPEP-BALANCE) is the premier energy systems analysis software in use in over 80 countries. ENPEP-BALANCE
was developed by CEEESA with support from the U.S. Department of
Energy. ENPEP-BALANCE allows users to evaluate the entire energy system (supply and demand side) and the environmental implications of different energy strategies. The
latest ENPEP-BALANCE version takes full advantage of the Windows operating environment.
The Windows version of the Energy and Power Evaluation Program (ENPEP-BALANCE) is the premier energy systems analysis software in use in over 80 countries. ENPEP-BALANCE
was developed by CEEESA with support from the U.S. Department of
Energy. ENPEP-BALANCE allows users to evaluate the entire energy system (supply and demand side) and the environmental implications of different energy strategies. The
latest ENPEP-BALANCE version takes full advantage of the Windows operating environment. GASMAP combines a geographic information system and a relational database system that provide information on the U.S. natural gas infrastructure. GASMAP can be used to locate the pipelines of any gas transmission company on a map at varying levels of detail. Users can then access Information on capacity (pipe diameter, length, and maximum operating pressure); flows (peak day, average day, receipt and delivery points, storage, and delivery volume); and financial parameters (gas purchases, gas prices, sales volumes, operating and maintenance costs, and balance sheet). Because GASMAP is loaded on a remote server, multiple users can access information from their own locations.
GASMAP combines a geographic information system and a relational database system that provide information on the U.S. natural gas infrastructure. GASMAP can be used to locate the pipelines of any gas transmission company on a map at varying levels of detail. Users can then access Information on capacity (pipe diameter, length, and maximum operating pressure); flows (peak day, average day, receipt and delivery points, storage, and delivery volume); and financial parameters (gas purchases, gas prices, sales volumes, operating and maintenance costs, and balance sheet). Because GASMAP is loaded on a remote server, multiple users can access information from their own locations. NGview decreases the time required to develop a natural gas network topology, including pipeline links (uni- or bi-directional) and pipeline nodes (e.g., delivery points, supply points, and interconnections). NGview helps link spatial and relational data sets, which could include thousands of pipeline segments and points. Once these links have been established, data can be updated with minimal effort, providing quick turnaround time for studies. The model’s database interface links to simulation tools, such as NGflow and NGcut. NGview greatly improves the viewing and understanding of simulation results because analysts can toggle between schematic and geographical information system views.
NGview decreases the time required to develop a natural gas network topology, including pipeline links (uni- or bi-directional) and pipeline nodes (e.g., delivery points, supply points, and interconnections). NGview helps link spatial and relational data sets, which could include thousands of pipeline segments and points. Once these links have been established, data can be updated with minimal effort, providing quick turnaround time for studies. The model’s database interface links to simulation tools, such as NGflow and NGcut. NGview greatly improves the viewing and understanding of simulation results because analysts can toggle between schematic and geographical information system views. NGdepletion addresses outage duration times and determines whether and when a component outage will affect a specific location or site. The model computes the amount of time that the line pack will be able to continue to supply gas. NGdepletion is used extensively in analyses of U.S. natural gas network issues and in studies of electricity-gas interdependency issues.
NGdepletion addresses outage duration times and determines whether and when a component outage will affect a specific location or site. The model computes the amount of time that the line pack will be able to continue to supply gas. NGdepletion is used extensively in analyses of U.S. natural gas network issues and in studies of electricity-gas interdependency issues. NGpressure determines how the loss of a critical link or node under various operating conditions might affect a natural gas system. The model addresses central issues such as: “Can the system continue to deliver gas to a certain location or site if a key city-gate is disrupted under both average and peak day conditions?” The model is based on the premise that the ability of a pipeline to deliver natural gas depends directly on operating pressure. NGpressure uses standardized industry equations and various data sources, and it is used extensively in analyses of issues associated with the U.S. natural gas network.
NGpressure determines how the loss of a critical link or node under various operating conditions might affect a natural gas system. The model addresses central issues such as: “Can the system continue to deliver gas to a certain location or site if a key city-gate is disrupted under both average and peak day conditions?” The model is based on the premise that the ability of a pipeline to deliver natural gas depends directly on operating pressure. NGpressure uses standardized industry equations and various data sources, and it is used extensively in analyses of issues associated with the U.S. natural gas network.